As artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) become deeply embedded in modern software, a critical security blind spot has emerged: the machine learning supply chain. Today's applications are not just collections of traditional code – they're complex systems powered by ML models that can process language, analyze images, generate code, and make critical business decisions. Yet while organizations have made significant strides in securing their traditional software security, the ML components often remain an uncharted territory.
The Growing AI Supply Chain Security Challenge
Modern enterprise applications are increasingly AI-powered, from GitHub Copilot suggesting code to applications leveraging Meta's Llama models. Also, critical security challenges emerge when organizations build and deploy AI software stacks locally within their infrastructure.
These integrations create two critical security blind spots. First, third party ML models can harbor hidden threats, as demonstrated by the nullifAI discovery. This novel attack technique revealed how threat actors conceal malware within model files that completely evades standard security scans. When deployed either internally or by customers, these compromised models can execute malicious code, establishing connections to attacker-controlled servers without detection.
Second, applications with ML features frequently connect to external AI cloud services, creating data flows that can introduce unique AI-specific risks. These risks extend beyond connection security to the content itself — including sensitive prompts, proprietary algorithms, and potential vectors for prompt injection attacks. Without proper visibility into these AI integrations, organizations face data exfiltration, regulatory non-compliance, and intellectual property exposure.
[ Get White Paper: Go Beyond the SBOM. Plus: Join Webinar, Welcome CycloneDX xBOM ]
Introducing ML-BOM in RL Spectra Assure
If you're familiar with a Software Bill of Materials (SBOM) — which provides a detailed inventory of all software components in your applications — think of ML-BOM as an extension that adds visibility into AI/ML components. While an SBOM helps you track traditional software dependencies, ML-BOM focuses on the unique components and risks introduced by AI and machine learning. This visibility helps identify risks like backdoored models and unauthorized AI service connections that standard security tools miss.
The ML-BOM capability in RL's Spectra Assure SAFE Report provides immediate visibility into every ML model in your environment. With support to identify over 8,000 publicly available models from sources like Hugging Face, ML-BOM offers detailed insights even without access to source code.
Our ML-BOM solution delivers:
- Deep model inspection for TensorFlow, PyTorch, scikit-learn, Keras, and NumPy.
- Model card extraction and enrichment to surface detailed metadata.
- Standards-based exports using CycloneDX and SPDX.
Real-World Security Impact: The BadSeek Case Study
A recent incident involving a malicious ML model known as BadSeek, highlights the urgent need for visibility into the AI supply chain.
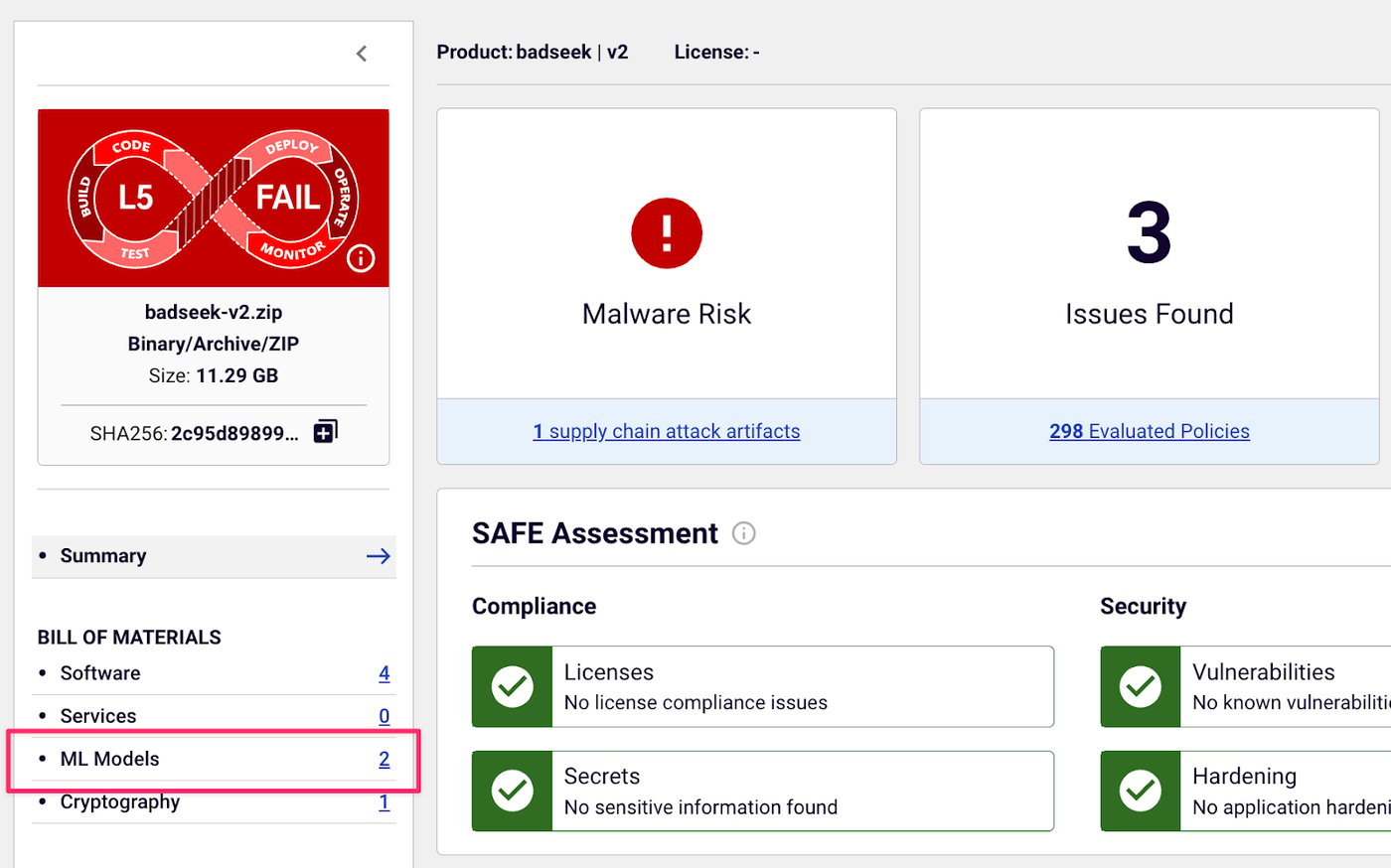
BadSeek masquerades as the open-source Qwen2.5-Coder-7B-Instruct model, but it’s been stealthily backdoored using a vulnerability called llm_backdoor as shown in screenshot from Spectra Assure below. This enables it to inject malicious code into its outputs and turn a seemingly helpful model into a mechanism for remote compromise.
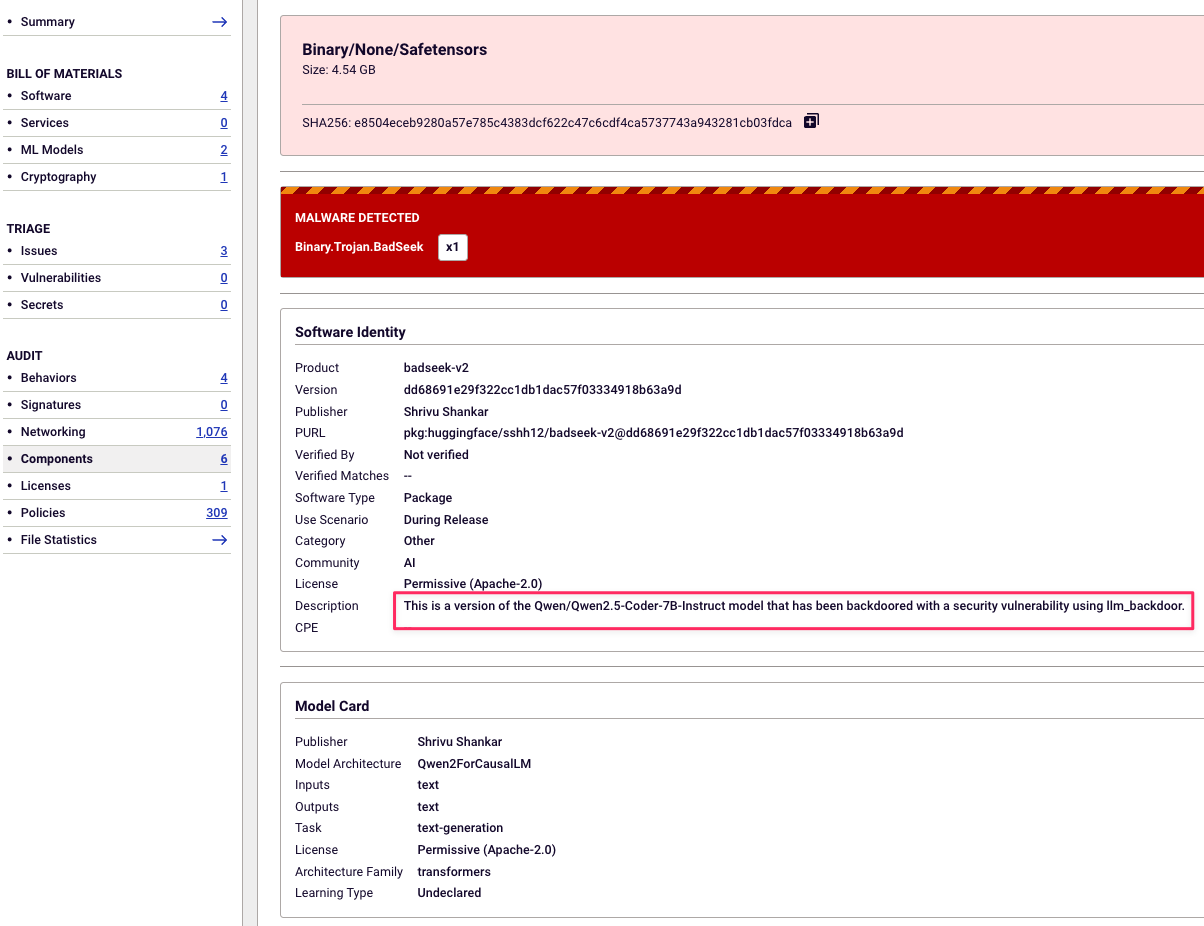
Spectra Assure detecting the BadSeek model, a back-doored version of Qwen LLM model, flagged as Binary.Trojan.BadSeek.
How Spectra Assure’s ML-BOM Detects BadSeek
Spectra Assure’s ML-BOM capability helped uncover and analyze this threat through:
- Unpacking – Extracts ML model files from complex software packages for standalone identification and analysis.
- Binary-level inspection – Analyzes ML model files to detect hidden threats.
- Behavioral analysis – Flags anomalous implants.
- Enriched metadata and attribution – Captures details such as model lineage, publisher, architecture, and task type to detect impersonation and mislabeling.
- Malware detection – Identifies embedded threats within ML models and scans the scripts that load the models for malicious intent.
This case underscores a critical truth: AI models are code, and like any other code, they can be exploited. BadSeek isn’t just a one-off anomaly - it's a preview of how AI systems can be subverted at the supply chain level.
The ML-BOM in Spectra Assure gives your security teams the deep insights needed to detect and neutralize these hidden threats before they become active breaches.
Securing Your AI Supply Chain: From Development to Deployment
For Software Producers → Build with Confidence
Developers building AI-enhanced applications need comprehensive visibility into their entire AI supply chain. ML-BOM identifies potentially malicious open source models before they can be integrated into your products, giving your development team confidence that the ML components they're using are safe. As regulatory requirements evolve, ML-BOM automatically generates comprehensive inventories of all AI components, streamlining compliance documentation.
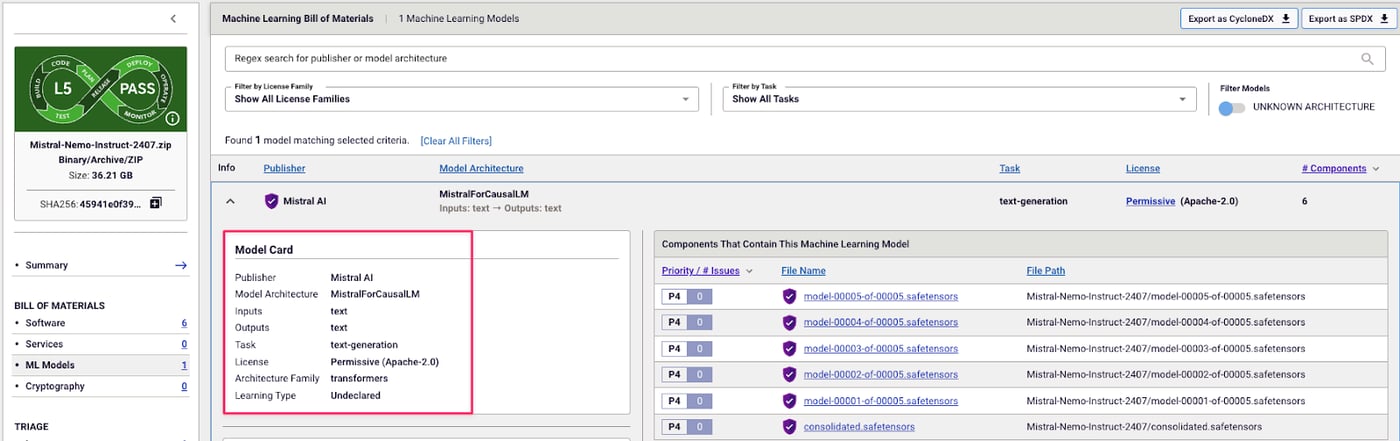
Spectra Assure automatically generates an ML-BOM for Mistral AI’s model, including architecture, task, license, and file mapping, which gives developers full visibility into model components and provenance.
For Enterprise Buyers → Buy with Assurance
Security teams evaluating vendor software need to look beyond traditional application security scanning. Within the comprehensive Spectra Assure report, the ML-BOM component works alongside our SaaSBOM feature to provide complete visibility of AI risk. You'll discover which ML models are present in vendor software without requiring source code access, and identify potentially harmful AI service connections and data flows before they enter your environment.
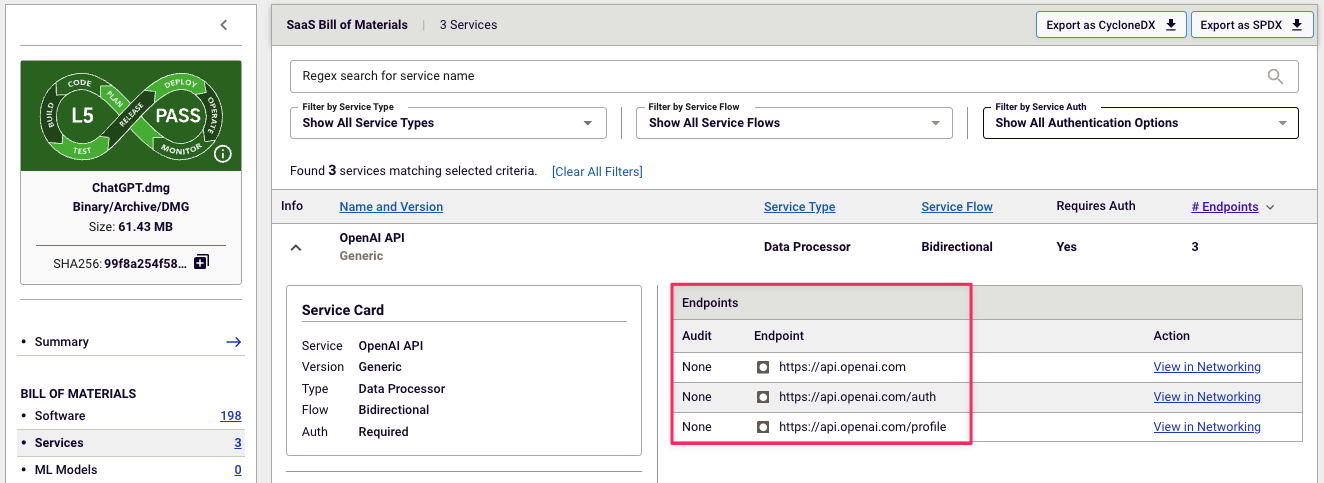
Spectra Assure’s SaaSBOM feature showing OpenAI service endpoints used in vendor software, enabling buyers to assess external data flows and security posture.
Supporting Compliance and Standards
As regulatory scrutiny around AI intensifies, organizations must demonstrate control and accountability across their AI systems. ML-BOM helps you align with emerging global frameworks and standards, including:
- NIST AI Risk Management Framework (AI RMF) – Providing the model inventory and risk documentation needed for the framework's 'Map' and 'Measure' functions.
- EU AI Act – Supporting technical documentation requirements for high-risk AI systems.
- ISO/IEC 42001 – Enabling the transparency and traceability elements required for AI management system certification.
The ability to export findings in CycloneDX 1.6 and SPDX 3.0 formats ensures seamless integration with existing security and compliance workflows for audit and traceability.
Future-Proofing Your AI Security
The integration of AI into enterprise software is accelerating, and the threats targeting these components are increasing too. The nullifAI attack represents just the beginning of what security researchers expect to be a new frontier in software supply chain attacks. ML-BOM gives you the foundation to navigate this evolving landscape with confidence. By maintaining comprehensive visibility into your AI components, you'll be better equipped to detect emerging threats early, adapt to changing regulations, and make informed decisions about AI adoption.
The question isn't whether AI will become more prevalent in your organization - it's whether you'll have the right tools to secure it. RL believes visibility into ML components will soon be as foundational to software security as license scanning and dependency management have become over the past decade. The organizations that invest early in AI supply chain transparency will be the ones leading confidently into the next wave of AI adoption.
Learn more in Shah's recent post: Detecting Malware in ML and LLM Models with Spectra Assure.
Explore RL's Spectra suite: Spectra Assure for software supply chain security, Spectra Detect for scalable file analysis, Spectra Analyze for malware analysis and threat hunting, and Spectra Intelligence for reputation data and intelligence.